Your shed’s life depends highly on the foundation you build for it. Even if you use top-quality materials for constructing the shed, it can quickly get damaged by water and insects if it is built on an improper foundation.
So crafting a long-lasting and sturdy base is the most important step in building a shed from scratch. Here are the best shed foundation options to maximize your building’s durability.
#6. Skid Foundation

- Shed remains portable
- Easy and fast to install
- Suitable for both small and large shed sizes
- Unsuitable for sloped land
- Higher chance of shed floor rotting
- Wet soil can cause the shed to sink over time
Making a skid foundation is the fastest way to build a shed base. Use pressure-treated lumber as skids.
Dig 6 inch deep trenches in the ground at the skid locations, and fill them with gravel to create a level base for your skids to sit on. Make sure to level the skids with each other.
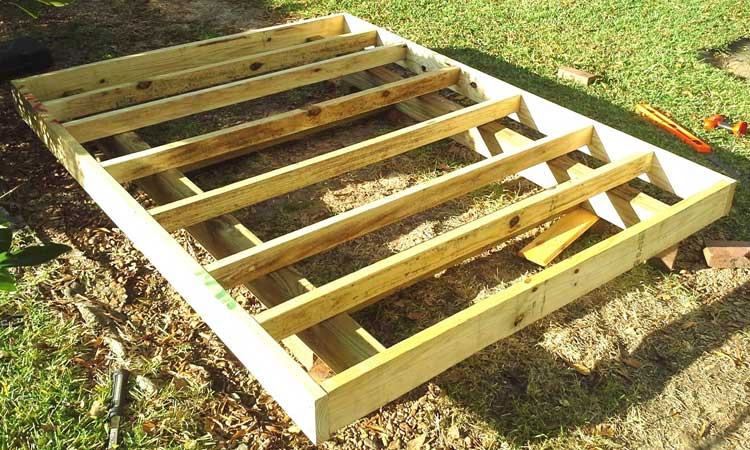
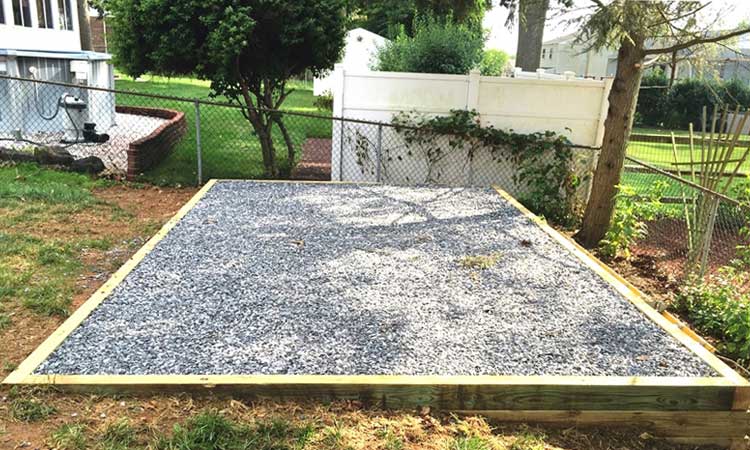
#5. Gravel Pad Foundation

- Gravel can be leveled fast
- Good for sheds without a floor
- Suitable for both small and large sheds
- Can be constructed quickly
- Higher chance of floor lumber rotting
- May need a separate ditch for water drainage
- Needs timber frame to hold gravel in place
- Unfit for sloped land
Build the timber frame to hold the gravel pad about 2 inches bigger than your shed’s dimensions. The gravel should be 6 inches thick and have smaller particles. This will make it easier to level and give a stable base.
#4. Concrete Blocks Foundation
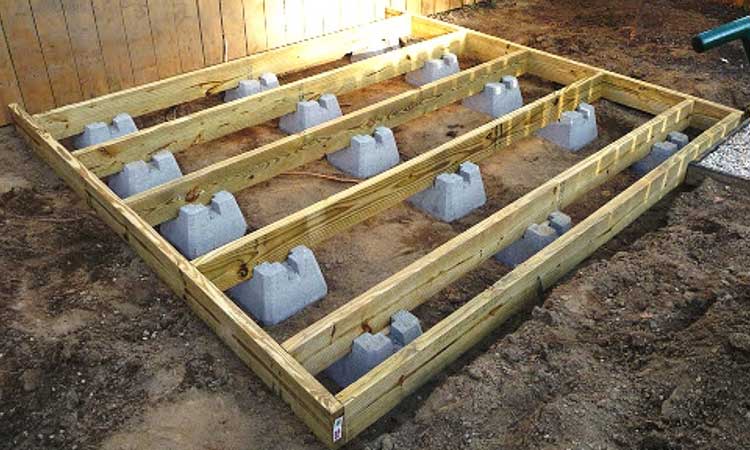

- Can be stacked and leveled quickly
- Suitable for all shed sizes
- Blocks available in different sizes
- Prolonged wet soil can cause blocks to sink
- Span of lumber between the blocks is left unsupported
- Unsuitable for highly sloped land
- Not ideal for storing heavy machinery or equipment that will vibrate the floor
Place concrete blocks for the base at the corners of your shed and at regular intervals along the perimeter. For sheds that will store really heavy equipment, you can place blocks at intervals of one foot or 6 inches. Make sure to carefully level each block and square the corners.
#3. Concrete Pier Foundation
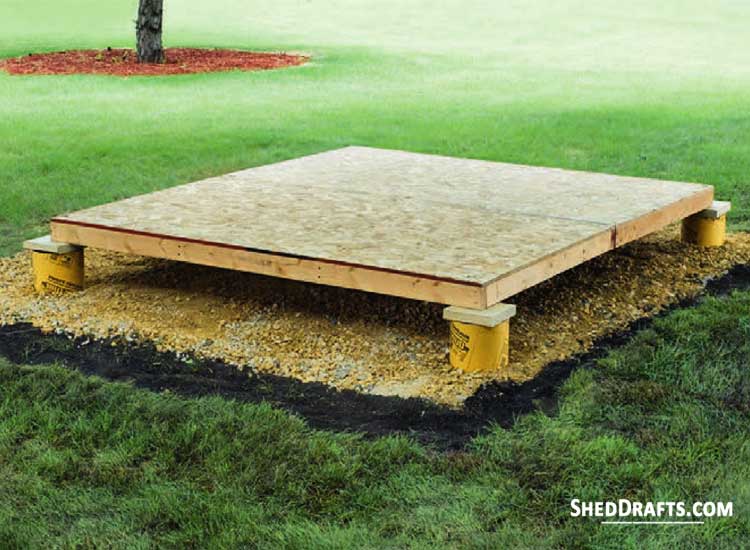

- Permanent Foundation
- Quick Construction
- Lower Cost With Higher Durability
- Long-term exposure to moisture can cause damage
- More complex to build compared to pavers or blocks
- Muddy ground may cause sagging and cracking in piers
Crafting a concrete pier foundation will give you the durability of a permanent foundation while keeping expenses low. Poured concrete forms will create a much more durable base for your shed compared to skids or gravel pads.
#2. Concrete Pavers Foundation
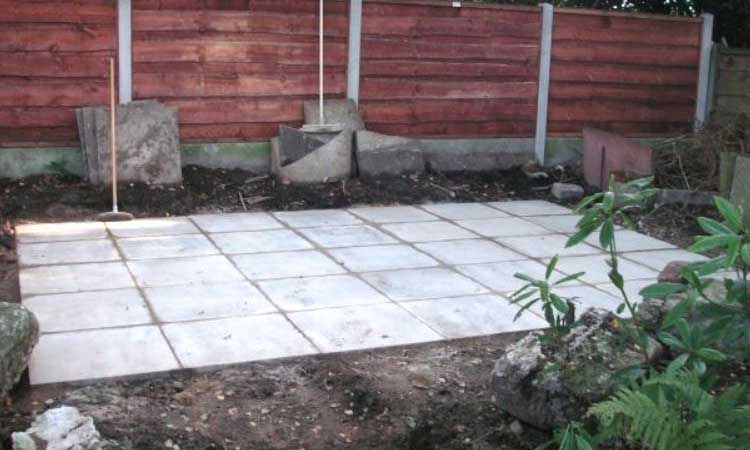

- Wide range of sizes, shapes, and colors available
- Simple and quick installation
- Shed walls can be secure directly to pavers
- Complete support for the entire shed floor frame
- Pavers may become uneven over time
- Heavy weights can cause pavers to crack
- Unsuitable for larger sheds
This is a simple shed foundation that any beginner can build. Pavers are best suitable for land which is almost level. You can lay a layer of sand underneath the pavers to level them if your ground is uneven. Add a layer of garden cloth underneath the pavers to prevent weed growth between the gaps.
#1. Concrete Slab Foundation
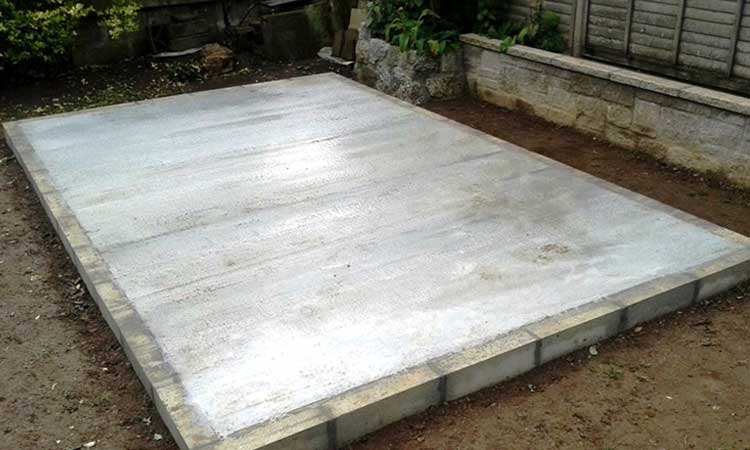

- Creates a rock-solid permanent foundation
- Supports really heavy weights
- Can be used directly as the shed floor
- Suitable for all shed sizes
- Cannot pour concrete in freezing weather
- May require a separate ditch for water drainage
- Unsuitable for sloped ground
This is the most durable and solid foundation you can build for your shed. The poured-concrete slab foundation can support really heavy loads like vehicles and machinery that can be driven directly into the shed.
Building a solid foundation will make sure your shed lasts many years with little maintenance. Having the right shed plans will help make the construction process quick and easy.